I. Introduction
Operating the press brake requires mastering different skills, and the requirements for the press brake operator are also very high. They should not only be able to use machines but also understand mathematics, read design drawings and learn machine programming, and more. This article will detail the work content, work requirements, and work prospects of the press brake operator.
II. What Does a Press Brake Operator Do
Simple Introduction to Press Brake
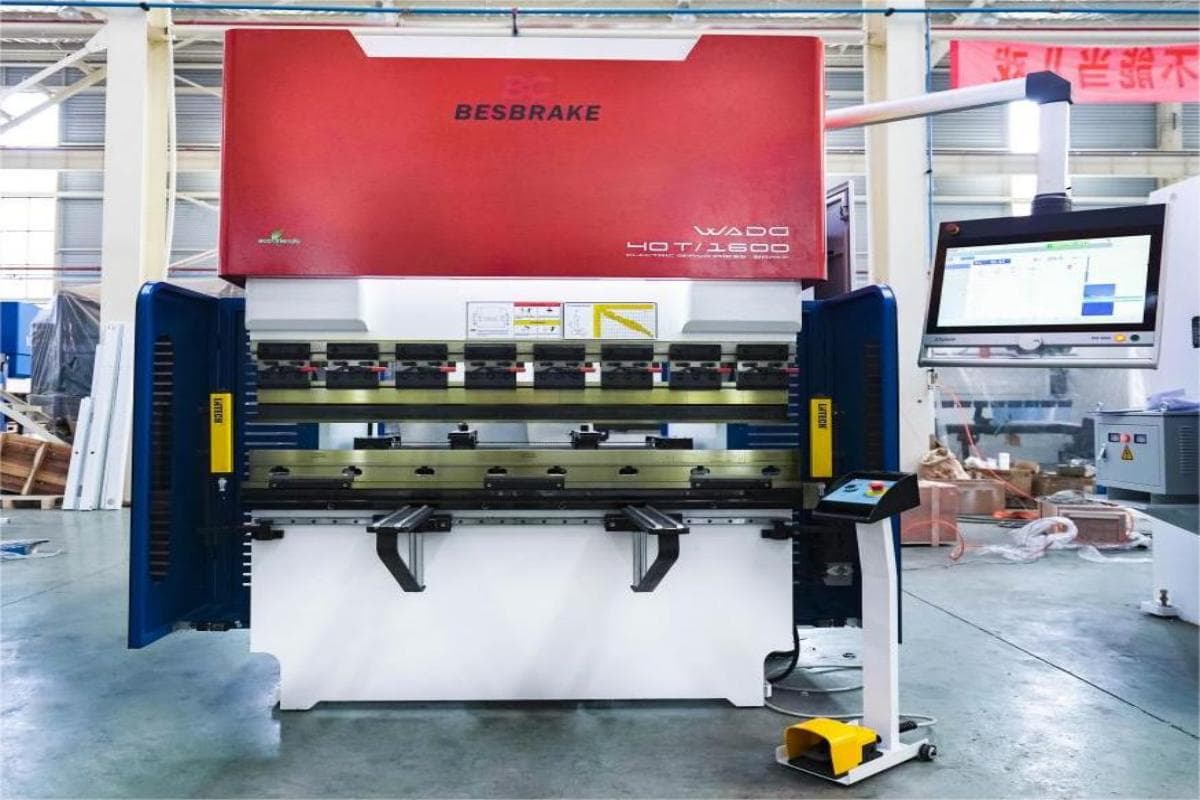

A Press Brake is a versatile machine primarily used for bending sheet metal, but it can also be utilized to form various materials such as plates, tubes, profiles, and even some non-metallic workpieces like plastics.
The machine applies pressure to the workpiece between a matching punch and die, causing it to bend or fold into the desired angle or shape according to the specific tooling set up.
Press brakes are essential equipment in the sheet metal fabrication industry, capable of creating a wide range of bends, from simple linear bends to complex multi-bend profiles, with high precision and repeatability.
It can be said that the press brake is the machine that makes the machine. The work of a press brake operator is mainly to operate the machine to bend, shape, and cut various metal materials. They may also need to use the shearing machine and laser cutting machine to cut sheet metal.
Duties and Responsibilities
Safety Operation
Strictly obey various safety operating regulations and correctly wear personal protective equipment, like goggles, gloves, etc. Seriously check the machine and its surrounding environment to ensure no safety risk. Always be vigilant during the operation. It is strictly prohibited to operate violating regulations or leaving the workplace.

Workpiece Preparation
According to the processing drawings and process requirements, prepare plates, pipes, and other workpieces to be processed. Check whether the workpiece's size, material, and surface quality meet the requirements, and perform preprocessing if necessary. Reasonably arrange and stack workpieces to facilitate quick and accurate loading and unloading.
Tooling Preparation
Select the appropriate bending tooling (punch and die) according to the bending process's requirements. Carefully check whether the tooling's shape, size, fit clearance, etc., meets the requirements to ensure no wear or defects. Install and adjust the tooling correctly to ensure it is firm and reliable, and calibrate it if necessary.
Machine Settings
Be proficient in operating various control panels and buttons of the press brakes and correctly select processing programs or input processing parameters.
According to the workpiece material, thickness, bending angle, etc., set the appropriate bending pressure, backgauge position, bending speed, etc. If necessary, perform trial bending to check whether the parameter settings are correct and make fine adjustments.
Bending Operation
Correctly place the workpiece so that it is accurately aligned with the tooling, and keep the workpiece smooth and symmetrical.
Start the press brake and observe the bending process to ensure that the workpiece is stressed smoothly and the bending line is positioned accurately.
Adjust parameters such as pressure and speed as appropriate to control the bending angle and quality. Take out the bent workpiece in time and check whether its size, angle, surface quality, etc. are qualified.
Quality Inspection
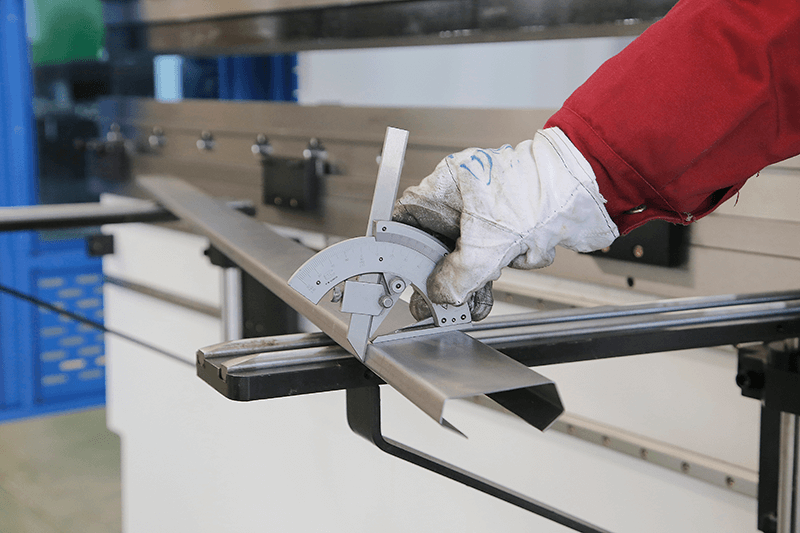

Use measuring tools such as vernier callipers, angle rulers, etc., to randomly check the key dimensions and angles of the bent workpieces. Inspect the bent workpiece's surface for scratches, indentations, cracks and other defects.
If substandard products are found, they should be isolated in time, the reasons analyzed, and process parameters adjusted or reported for processing.
Equipment Maintenance
Perform routine inspections on the press brake every shift or every day, such as checking oil levels, filters, electrical connections, etc. Keep the machine and working environment clean and hygienic, and clean up debris, oil, etc. in a timely manner.
If any equipment malfunction or abnormality is discovered, it must be promptly reported for repair, and operation while sick is not allowed.
Record and Communicate
Fill in various production record forms as required, such as bending processing orders, quality inspection reports, equipment inspection forms, etc.
Maintain good communication with superiors, colleagues, and other departments to coordinate and solve production problems. Provide rational suggestions to optimize the bending process and improve production efficiency and quality.
III. Skills and Qualifications
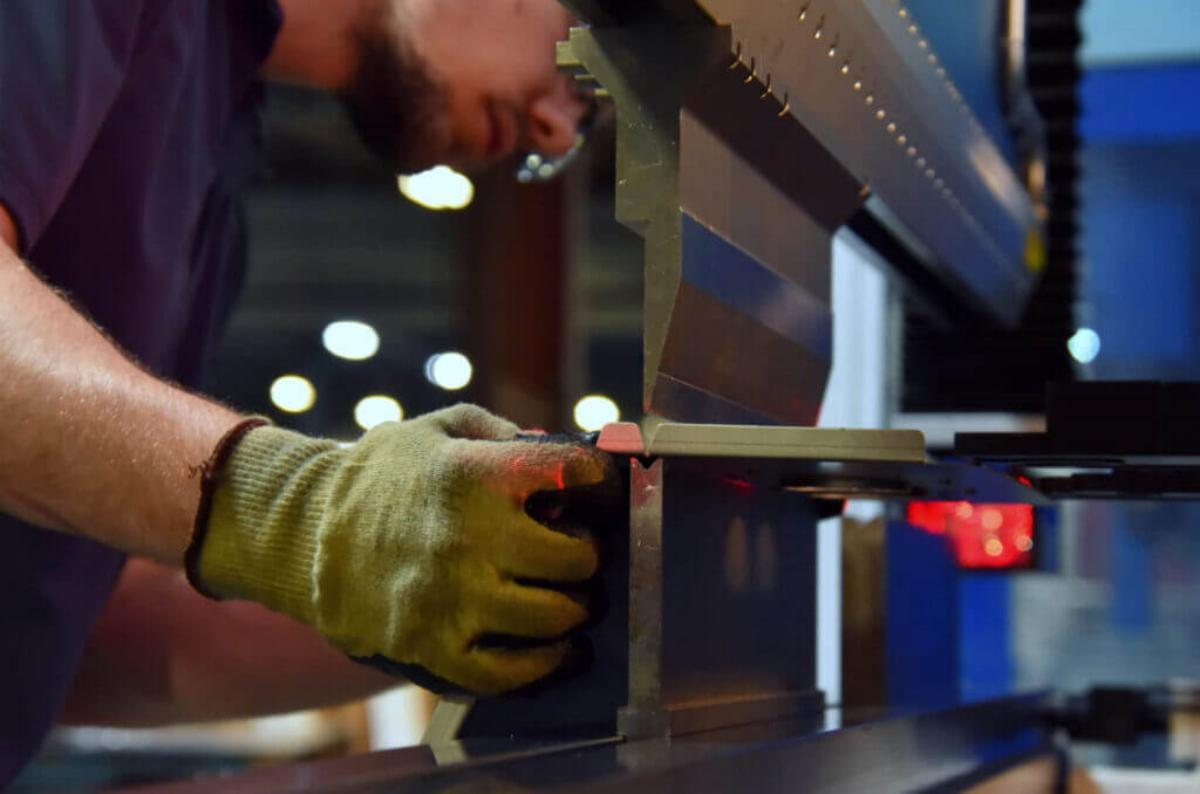

Understanding Tooling and Machines
Press brake operators need to understand the various tools used for the machine, as there are many kinds of press brake toolings. Choosing the wrong tooling will lead to different bending results. Here are some common types of dies and their selection principles:
V-shaped Dies
V-shaped dies are the most commonly used bending dies, suitable for most materials and thicknesses. The larger the V-opening, the larger the bending radius, and the smaller the impact on the material, but it also takes up more space. Generally speaking:
- For thin materials (≤6mm), choose a V-opening width 6-8 times the material thickness
- For thick materials (>6mm), choose a V-opening width 8-12 times the material thickness
U-shaped Dies
U-shaped dies are suitable for bending high-strength materials or smaller bending radii. Compared with V-shaped dies, U-shaped dies provide a larger supporting area and reduce stress concentration on the material. However, U-shaped dies have higher requirements for die positioning accuracy and are prone to springback.
Ball Nose Dies
Ball nose dies are specifically used for 180° bends and can complete the bend in one step, which is highly efficient but only suitable for thin materials. The radius of the ball nose die is generally controlled within 1-2 times the material thickness.
Custom Dies
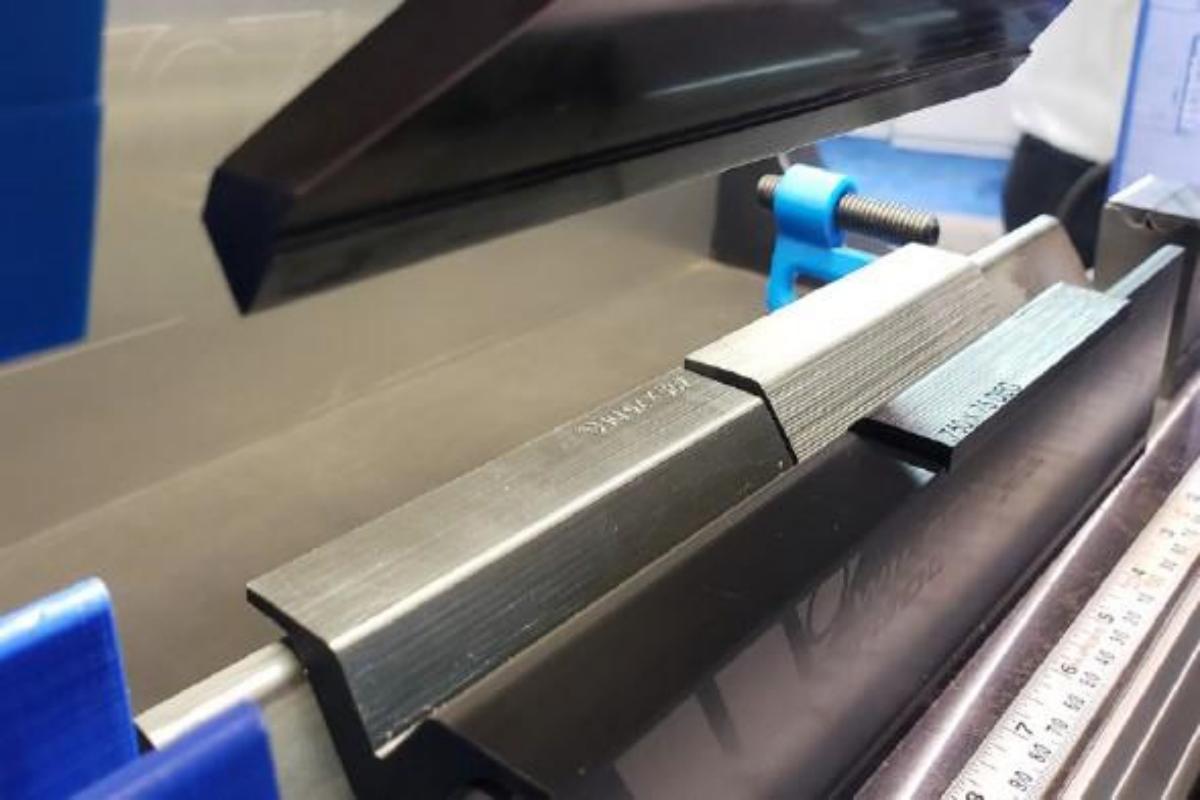

For some irregular bends, custom dies are required. Although custom dies have a higher cost, they can significantly improve production efficiency and processing accuracy.
Press brake operators also need to know different bending methods, such as air bending, bottom bending, and coining. At the same time, the press brake operator should also know the tonnage limit of the press brakes.
Exceeding the range of bending force will cause damage to the machine. Press brake operators need to know the type, structure, and working principle of press brake machines very well.
There are different types of press brakes, such as mechanical press brake, hydraulic press brake, electric servo press brake, CNC press brake, pneumatic press brake, CNC panel bender, etc. Press brake operators should be familiar with the differences, advantages, and disadvantages of different types of press brakes.
Using different press brakes to process different metal plates can improve production efficiency and reduce production costs. The press brake operator should be able to understand the workpiece drawing and work according to the tolerance of metal materials.
The use of CAD drawings can not only ensure the accuracy of bending workpieces but also improve bending efficiency. The computer skills of the press brake operator are very important, and it is necessary to proficiently master the computer program editing ability.
Must have certain mathematical calculation abilities, including measuring and calculating dimensions. To ensure the accuracy of the workpiece, it is necessary to learn to use a caliper in order to perform contour measurements.
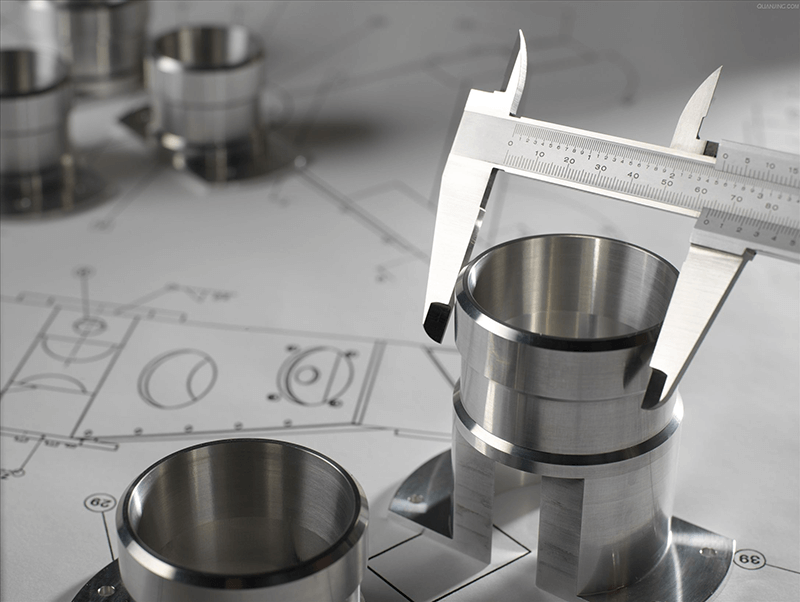

Job Qualifications
Most press brake operators are not highly educated, and usually, a high school diploma is enough. However, this does not mean that the work of the press brake operator is simple. It still requires a high sense of responsibility and attention to detail.
Press brake operators need to have a computer and mathematical knowledge to demonstrate their hands-on ability and analytical skills. Additionally, they should be able to stand for long periods and have enough physical strength to handle materials.
Generally, press brake operators work in a noisy environment, but they must be able to focus on details. They need to pay close attention to the operation process and subtle changes in metal plates.

Training and Certification Requirements for Press Brake Operators
Press brake operators are usually required to accept professional skills training, which can assist them in mastering knowledge of the bending principle, technique, and quality control.
Some big enterprises will establish an internal training system, train new employees, and offer practical operation training. At the same time, some professional institutes, like PMA and VDMA, will offer press brake operation training and certificate courses.
Through these courses of learning and testing, operators can acquire internationally recognized professional qualification certificates, such as the EuroBlech certificate etc. These certificates not only prove the operators' skills level but are also beneficial to their career development and salary increase.
The press brake operator needs to strictly follow various safety measures to prevent safety accidents from occurring. At the same time, you also need to participate in some safety training, machine operation training, etc.
The use of safety devices can also reduce risks, including light curtain protection, two-hand control devices, retraction devices, restraint devices, etc.
Salary Expectations
The income of press brake operators is determined by many factors, including relevant experience and technology, working time, company size, and more. Wages gradually increase from junior press brake workers to skilled workers.
IV. Case: 90° Bending of Stainless Steel Sheet
Workpiece Parameters
- Material: 304 stainless steel
- Thickness: 4mm
- Bending angle: 90°
- Bending length: 1000mm
Operation Key Points
Die Selection
- Choose a V-shaped die with a V-opening width of 8 times the sheet thickness, which is 32mm. This ensures bending quality while avoiding excessive impact force.
- The die length should be the bending length + 3 times the sheet thickness, which is 1012mm, to prevent edge deformation.
Bending Force Calculation
- The tensile strength of 304 stainless steel is 600MPa, and the bending width is 1000mm. The bending force F = 0.4 × tensile strength × thickness^2 × bending width ÷ V-opening width
- Substituting the data, F = 0.4 × 600 × 4^2 × 1000 ÷ 32 = 300kN
- Choose a press brake with a capacity above 350kN to have some margin
Bending Compensation
- The springback rate of 304 stainless steel is about 15%, so it is necessary to overbend by 15%, which is 103.5°
- Set the bending angle to 103.5° on the press brake to compensate for spring back
Bending Speed Control
- 304 stainless steel is a difficult-to-process material, and the bending speed should not be too fast, generally controlled at 5-8mm/s
- Excessive bending speed will aggravate die wear and affect bending accuracy
Die Lubrication
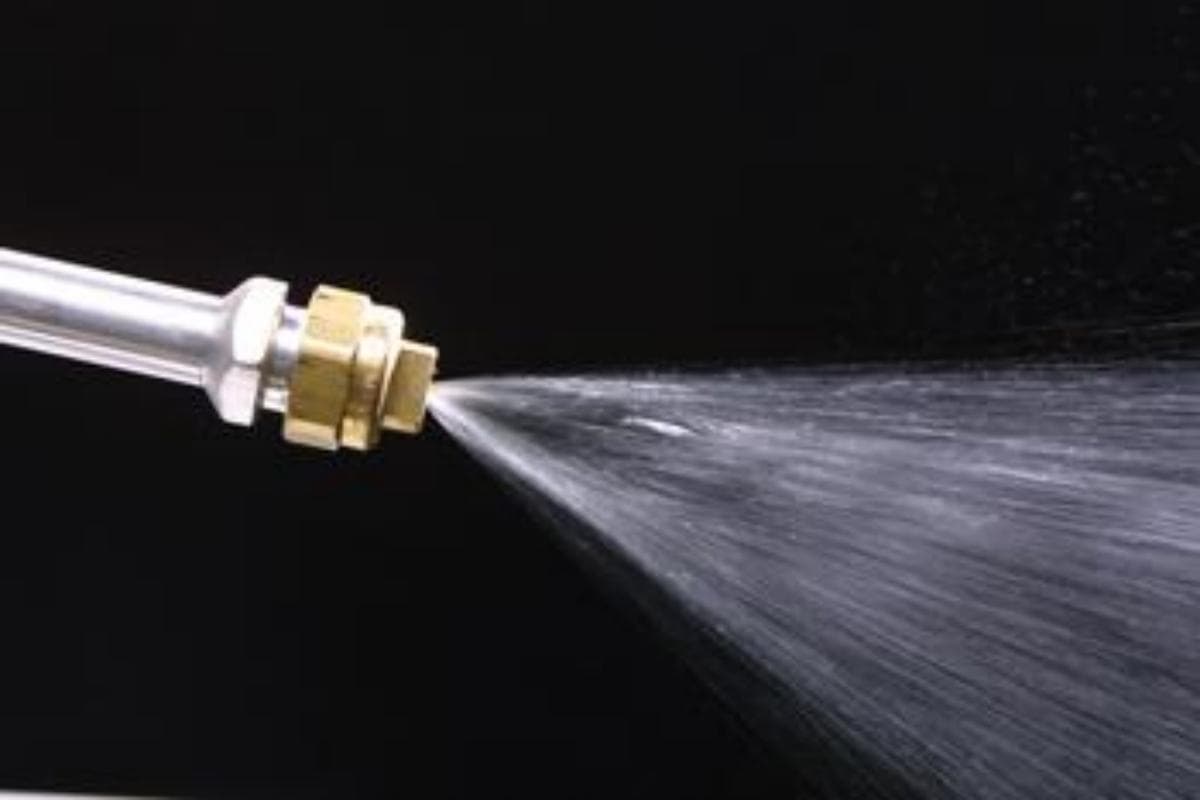

- Stainless steel tends to stick to the die, affecting the bending quality, so a layer of lubricating oil needs to be applied to the die surface.
- Choose low-viscosity mineral oil or synthetic oil, and avoid using vegetable oil because it is prone to oxidative deterioration
Post-Bending Treatment
- After bending stainless steel, the bending area will undergo some hardening, and the toughness will decrease.
- If there are high plasticity requirements for the bending area, annealing treatment can be performed to restore the material's ductility.
By following the above operation key points, the 90° bending quality of a 4mm thick 304 stainless steel sheet can be ensured. Of course, in actual operation, it is also necessary to make fine adjustments according to equipment conditions and production requirements, which requires the operator to control flexibly based on experience.
V. How to Become A Press Brake Operator
Firstly, if you want to be an excellent press brake operator, you need to have some basic knowledge such as mathematics, machinery, computers, and other related areas. You should also understand different metal materials and their characteristics, and learn how to read and understand CAD drawings.
It's also important to understand the structure and working principle of the press brake. Once you have acquired this knowledge, the company will train the operators on the operation of the machine.
Press brake operators must also learn how to make complex workpieces through machine programming. In short, it's important to constantly learn new technologies and take additional training courses to improve your competitiveness in the industry.
Career Path
Preliminary Operator: familiar with the basic operation of press brake and can independently accomplish the simple workpiece bending. Know the common material bending properties and master the basic tooling selection principle. Able to measure the size and quality identify according to the drawing.
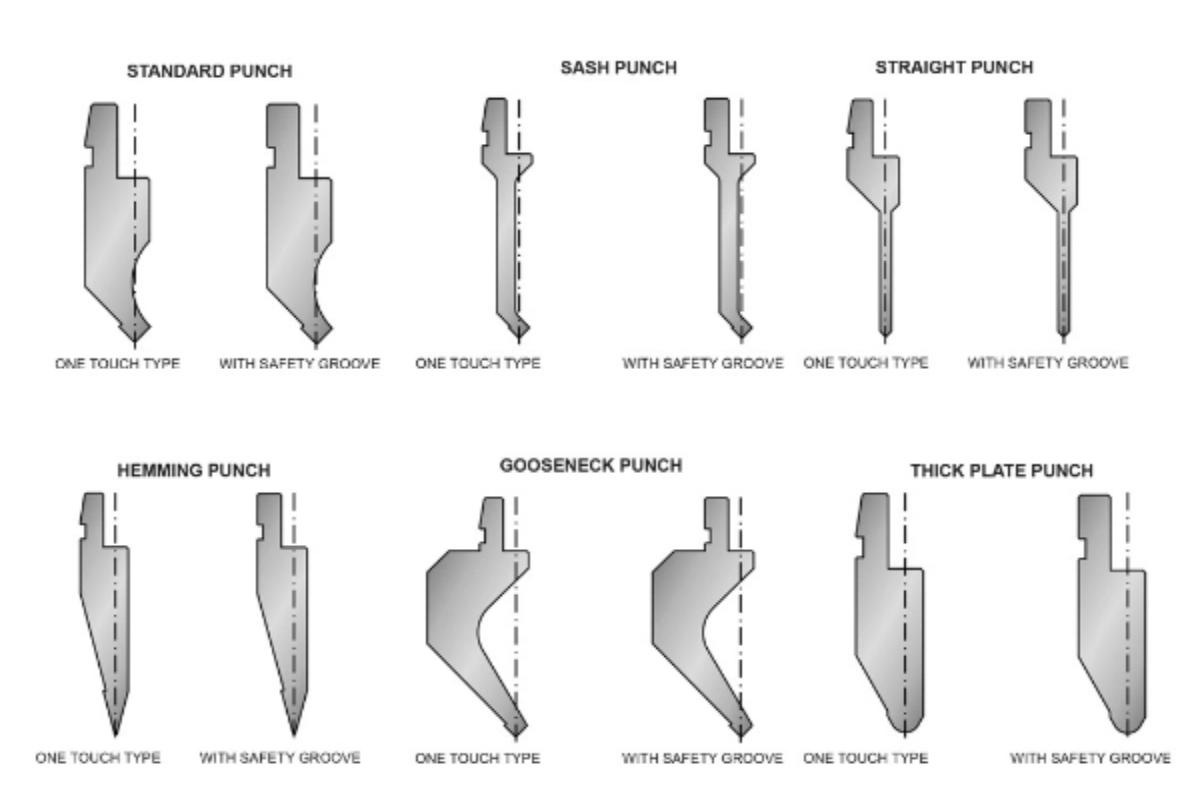
Intermediate Operator: able to handle some complex bending workpieces, such as multiple bending and special-shaped bending; master bending process setting and optimization, improving production efficiency and quality; master some troubleshooting, diagnosis, and maintenance ability, which can handle common machine problems.
Senior Operator: proficient in the bending process of various materials and able to handle difficult bending tasks. Has design and innovation capabilities for bending processes and continuously optimizes the production process. Able to guide and train junior and intermediate operators to improve the team's overall skill level.
Bending engineer: engage in R&D and research on bending processes and solve key technical problems. Optimize the layout and process of the bending production line to improve production efficiency and flexibility. Participate in the process design and trial production of new products to shorten the product development cycle.
Production management personnel: responsible for the daily management of the bending workshop and reasonable allocation of personnel and equipment resources. Develop production plans and quality goals, and supervise and evaluate the process. Promote the standardization and leanness of bending processes and continuously improve production performance.
VI. The Future of Press Brake Operators

If press brake operators want to develop in the industry for a long time, they need to keep up-to-date with the latest industry developments at all times.
This way, they can improve their understanding of the industry, enhance their technology skills, and increase their industry knowledge. Automation is increasingly being used in the sheet metal industry.
Enterprises will purchase automated equipment to improve production efficiency. Press brake operators should be able to use automation systems, including machine programming and other functions.
Press brake operators should have enough skilled experience and obtain certification from authoritative institutions. This will give them more competitive advantages in the job hunting process.
New requirements for automation and intelligence
With industrial 4.0 and development for intelligence, press brake automation and intelligence degrees have been improved. This arouses new requirements for press brake operators:
Digital ability: Familiar with digitally designed software like CAD/CAM, able to perform digital modeling and simulation of bending processes. Understand digital manufacturing systems, such as MES, ERP, etc., and be able to collect and analyze production data.
Automation control ability: master the press brake automation line operation and programming, know the PLC, sensor, which can handle simple production data collection and analysis.
Intelligent optimization capabilities: use big data and artificial intelligence technology to optimize bending process parameters intelligently. Develop an intelligent bending process APP to realize the sharing and promotion of process knowledge.
Flexible production capabilities: Adapt to the flexible production needs of multiple varieties, small batches, and short delivery times and quickly complete process switching. Collaborate with product design, process planning, and other departments to achieve product life cycle management.
Revitalize Skin NMN 18000 Capsules,Reduces Spots NMN 18000 Capsules,Reduces Wrinkles NMN 18000 Capsules
Shanghai Canal International Trade Co.,Ltd , https://www.nmncanal.com
